Vision-and-Language Navigation (VLN) relies heavily on the sim-to-real paradigm, and 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) stands out for its photorealistic real-time rendering ability, which is crucial for narrowing the sim-to-real gap. However, existing 3DGS lacks fine-grained object semantics and physical executability, making it unsuitable for practical VLN tasks.
We propose ![]() SAGE-3D, a novel paradigm that upgrades 3DGS into an executable environment foundation aligned with semantics and physics. It consists of two core components: Object-Level Semantic Grounding that enriches 3DGS with dense object-level annotations, and Physics-Aware Execution Jointing that embeds collision bodies and builds rich physical interaction interfaces.
SAGE-3D, a novel paradigm that upgrades 3DGS into an executable environment foundation aligned with semantics and physics. It consists of two core components: Object-Level Semantic Grounding that enriches 3DGS with dense object-level annotations, and Physics-Aware Execution Jointing that embeds collision bodies and builds rich physical interaction interfaces.
We also release two key resources to advance related research: ![]() InteriorGS, a dataset with 1,000 annotated indoor 3DGS scenes that covers mostly furnished indoor environments plus venues like concert halls and amusement parks, totaling over 554k object instances across 755 categories; and
InteriorGS, a dataset with 1,000 annotated indoor 3DGS scenes that covers mostly furnished indoor environments plus venues like concert halls and amusement parks, totaling over 554k object instances across 755 categories; and ![]() SAGE-Bench, the first 3DGS - based VLN benchmark featuring 2 million trajectory-instruction pairs, a hierarchical instruction pipeline, three novel navigation continuity metrics, and 554k detailed collision bodies. Experiments verify that SAGE-3D enhances model generalizability significantly, providing a solid foundation for embodied navigation research.
SAGE-Bench, the first 3DGS - based VLN benchmark featuring 2 million trajectory-instruction pairs, a hierarchical instruction pipeline, three novel navigation continuity metrics, and 554k detailed collision bodies. Experiments verify that SAGE-3D enhances model generalizability significantly, providing a solid foundation for embodied navigation research.
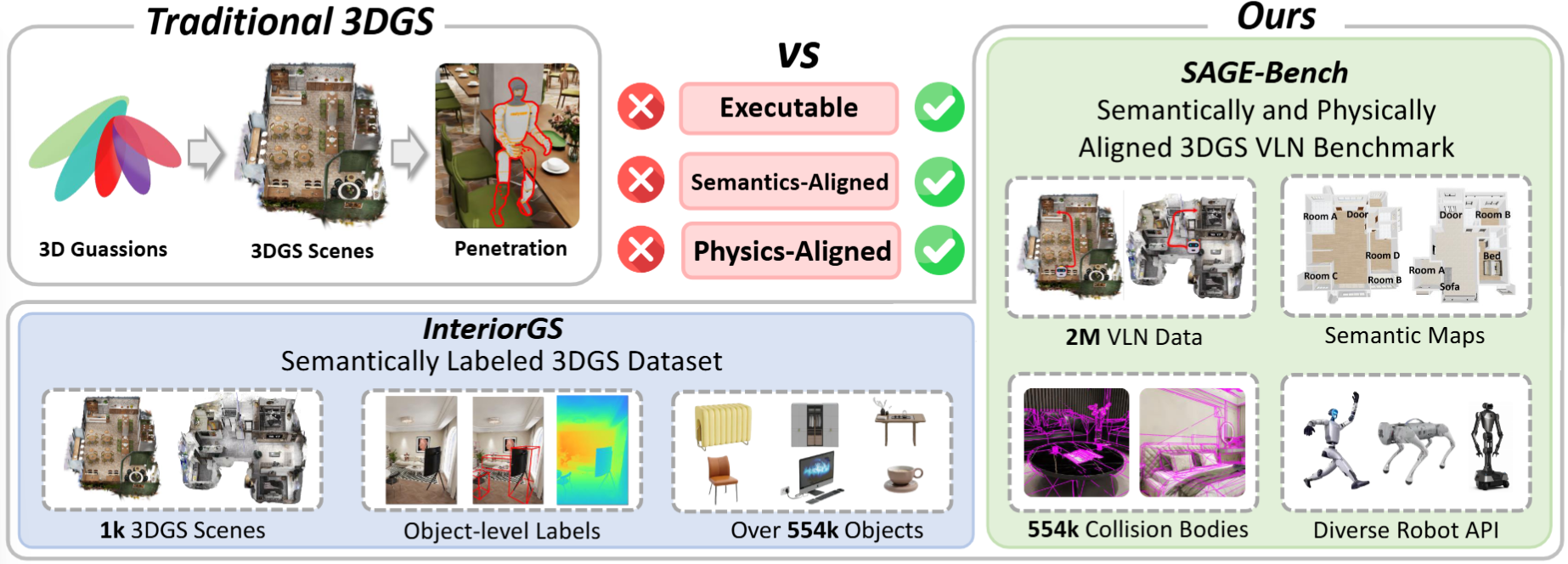
Vision-and-Language Navigation (VLN) relies on environment foundations that bridge simulation and real-world execution — and 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has emerged as a promising candidate for its photorealistic real-time rendering. However, traditional 3DGS falls short as an embodied learning base: it lacks fine-grained semantic annotations (e.g., object-level labels) and physical executability (evidenced by issues like agent penetration), failing to support practical embodied agent interaction and navigation.
To address this gap, we build two core resources that upgrade 3DGS into a semantically and physically aligned embodied environment:
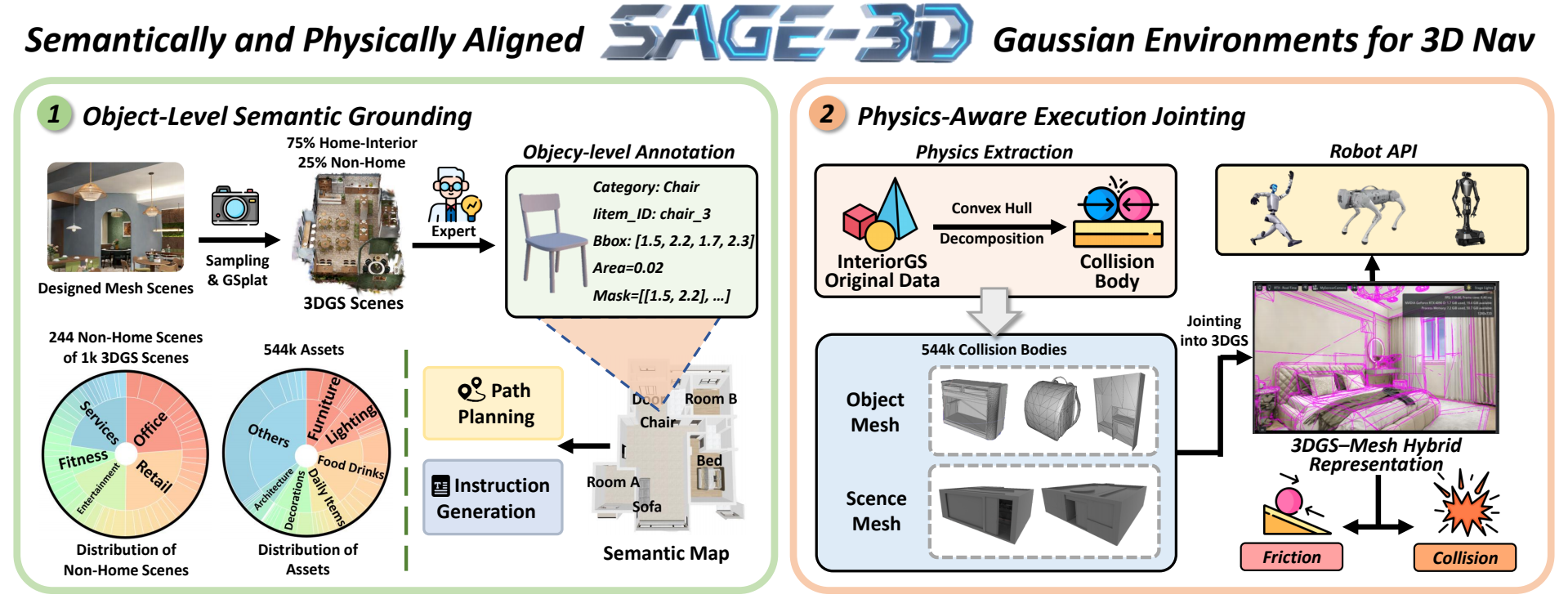
To upgrade 3DGS into an executable embodied environment, SAGE-3D relies on two key pipelines that address traditional 3DGS’s semantic and physical limitations:
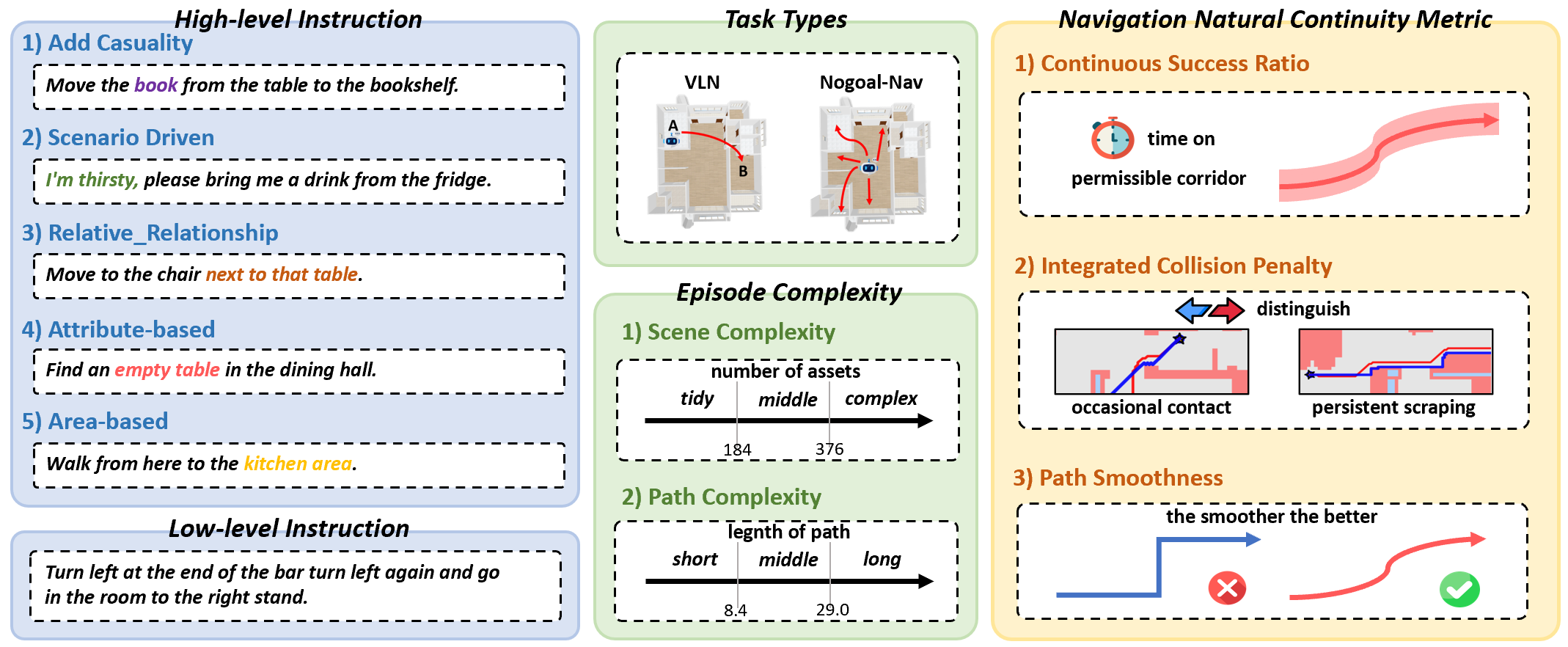
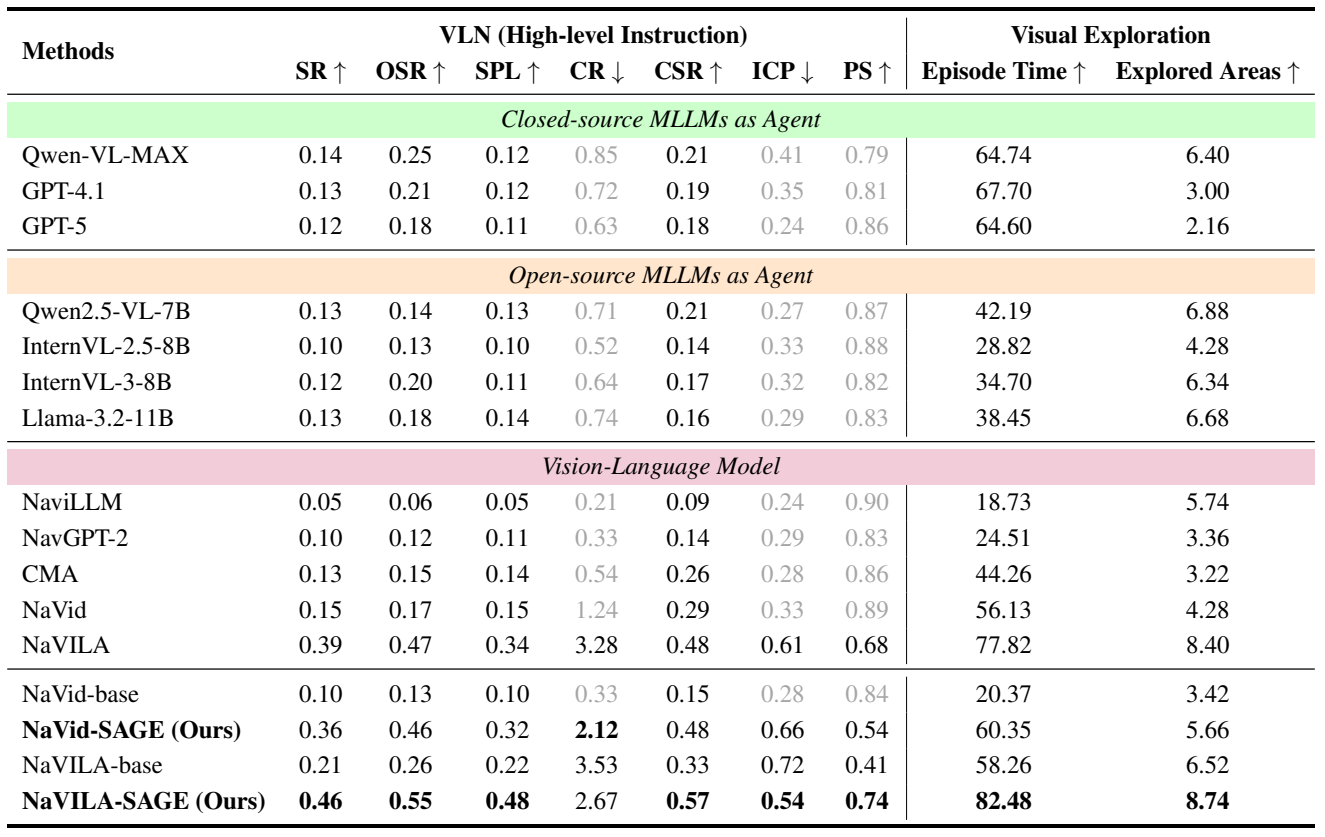
SAGE-Bench is the pioneering VLN benchmark built on 3DGS, featuring 2 million instruction–trajectory pairs and 554k detailed collision bodies. Its core highlights lie in the hierarchical instruction system and three novel navigation natural continuity metrics, which effectively support the evaluation of VLN models in complex scenarios.
@misc{miao2025physicallyexecutable3dgaussian,
title={Towards Physically Executable 3D Gaussian for Embodied Navigation},
author={Bingchen Miao and Rong Wei and Zhiqi Ge and Xiaoquan sun and Shiqi Gao and Jingzhe Zhu and Renhan Wang and Siliang Tang and Jun Xiao and Rui Tang and Juncheng Li},
year={2025},
eprint={2510.21307},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CV},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2510.21307},
}